Abstract
Review Article
Impact of Microplastics on Human Health through the Consumption of Seafood: A Review
Neeraj Kumar* and Dev Brat Mishra
Published: 14 June, 2025 | Volume 9 - Issue 1 | Pages: 015-019
Microplastics (MPs) pose a significant risk to human health, particularly through seafood consumption. Once ingested, MPs can spread from the digestive system to other organs via phagocytosis and endocytosis, leading to toxicological effects. Accumulation of MPs in tissues causes swelling, blockages, oxidative stress, and Cytotoxicity. Studies show MPs alter metabolism, disrupt immune function, and contribute to autoimmune diseases. Chronic exposure has been linked to neurotoxicity, vascular inflammation, and increased cancer risk due to DNA damage. MPs can cross biological barriers, including the placenta, affecting fetal development. Additionally, they serve as vectors for pollutants and bacteria, further complicating health risks. MPs in the bloodstream can trigger inflammatory responses, endothelial adhesion, and red blood cell coagulation, leading to cardiovascular complications. In vitro studies indicate MPs impair renal function and cause long-term inflammation in distal tissues. Moreover, oxidative stress caused by MPs plays a critical role in carcinogenicity. Despite growing evidence of adverse health effects, further research is necessary to understand the full impact of MPs’ exposure on human health and develop effective mitigation strategies.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001036 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Microplastics; Oxidative stress; Neurotoxicity; Cytotoxicity; Other tissues
References
- Naji A, Esmaili Z, Mason SA, Vethaak AD. The Occurrence of Microplastic Contamination in Littoral Sediments of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2017;24(25):20459–68. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9587-z
- Kor K, Ghazilou A, Ershadifar H. Microplastic Pollution in the Littoral Sediments of the Northern Part of the Oman Sea. Mar Pollut Bull. 2020;155:111166. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111166
- Kor K, Mehdinia A. Neustonic Microplastic Pollution in the Persian Gulf. Mar Pollut Bull. 2020;150:110665. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110665
- Neves D, Sobral P, Ferreira JL, Pereira T. Ingestion of MPs by Commercial Fish off the Portuguese Coast. Mar Pollut Bull. 2015;101(1):119–26. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.11.008
- Wang J, Tan Z, Peng J, Qiu Q, Li M. The Behaviors of MPs in the Marine Environment. Mar Environ Res. 2016;113:7–17. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2015.10.014
- Wright SL, Thompson RC, Galloway TS. The Physical Impacts of MPs on marine Organisms: a Review. Environ Pollut. 2013;178:483–92. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.031
- Karbalaei S, Hanachi P, Walker TR, Cole M. Occurrence, Sources, Human Health Impacts and Mitigation of Microplastic Pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2018;25(36):36046–63. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3508-7
- Brennecke D, Ferreira EC, Costa TM, Appel D, da Gama BA, Lenz M. Ingested Microplastics (>100 μm) Are Translocated to Organs of the Tropical Fiddler Crab Uca Rapax. Mar Pollut Bull. 2015;96(1-2):491–5. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.05.001
- Manzoor J, Sharma M, Sofi IR, Dar AA. Plastic Waste Environmental and Human Health Impacts. In: Handbook of Research on Environmental and Human Health Impacts of Plastic Pollution. Hershey, USA: IGI Global; 2020. p. 29–37. Available from: https://www.igi-global.com/chapter/plastic-waste-environmental-and-human-health-impacts/233346
- Prata JC, da Costa JP, Lopes I, Duarte AC, Rocha-Santos T. Environmental Exposure to MPs: An Overview on Possible Human Health Effects. Sci Total Environ. 2020;702:134455. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134455
- Galloway TS. Micro- and Nano-Plastics and Human Health. In: Marine Anthropogenic Litter. Cham: Springer; 2015. p. 343–66. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16510-3_13
- Schirinzi GF, Pérez-Pomeda I, Sanchís J, Rossini C, Farré M, Barceló D. Cytotoxic Effects of Commonly Used Nanomaterials and MPs on Cerebral and Epithelial Human Cells. Environ Res. 2017;159:579–87. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.08.043
- Wright SL, Kelly FJ. Plastic and Human Health: a Micro Issue? Environ Sci Technol. 2017;51(12):6634–47. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00423
- Anbumani S, Kakkar P. Ecotoxicological Effects of Microplastics on Biota: a Review. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2018;25(15):14373–96. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1999-x
- Smith M, Love DC, Rochman CM, Neff RA. MPs in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2018;5(3):375–86. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-018-0206-z
- Yan Z, Liu Y, Zhang T, Zhang F, Ren H, Zhang Y. Analysis of Microplastics in Human Feces Reveals a Correlation between Fecal Microplastics and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Status. Environ Sci Technol. 2021;56(1):414–21. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c03924
- Wu S, Wu M, Tian D, Qiu L, Li T. Effects of Polystyrene Microbeads on Cytotoxicity and Transcriptomic Profiles in Human Caco-2 Cells. Environ Toxicol. 2020;35(4):495–506. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22885
- Kirstein IV, Kirmizi S, Wichels A, Garin-Fernandez A, Erler R, Löder M, et al. Dangerous Hitchhikers? Evidence for Potentially Pathogenic Vibrio Spp. On Microplastic Particles. Mar Environ Res. 2016;120:1–8. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.07.004
- Crawford CB, Quinn B. The Interactions of Microplastics and Chemical Pollutants. In: Microplastic Pollutants. Vol 1. 2017. p. 131–57. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809406-8.00006-2
- Kelly FJ, Fussell JC. Size, Source and Chemical Composition as Determinants of Toxicity Attributable to Ambient Particulate Matter. Atmos Environ. 2012;60:504–26. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.06.039
- Valavanidis A, Vlachogianni T, Fiotakis K, Loridas S. Pulmonary Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Cancer: Respirable Particulate Matter, Fibrous Dusts and Ozone as Major Causes of Lung Carcinogenesis through Reactive Oxygen Species Mechanisms. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2013;10(9):3886–907. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10093886
- Forte M, Iachetta G, Tussellino M, Carotenuto R, Prisco M, De Falco M, et al. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Internalization in Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells. Toxicol Vitro. 2016;31:126–36. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2015.11.006
- Gewert B, Plassmann MM, MacLeod M. Pathways for Degradation of Plastic Polymers Floating in the marine Environment. Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2015;17(9):1513–21. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EM00207A
- Inkielewicz-Stepniak I, Tajber L, Behan G, Zhang H, Radomski MW, Medina C, et al. The Role of Mucin in the Toxicological Impact of Polystyrene Nanoparticles. Materials. 2018;11(5):724. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050724
- Sternschuss G, Ostergard DR, Patel H. Post-implantation Alterations of Polypropylene in the Human. J Urol. 2012;188(1):27–32. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.02.2559
- Geiser M, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Kapp N, Schürch S, Kreyling W, Schulz H, et al. Ultrafine Particles Cross Cellular Membranes by Nonphagocytic Mechanisms in Lungs and in Cultured Cells. Environ Health Perspect. 2005;113(11):1555–60. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8006
- Yacobi NR, DeMaio L, Xie J, Hamm-Alvarez SF, Borok Z, Kim KJ, et al. Polystyrene Nanoparticle Trafficking across Alveolar Epithelium. Nanomedicine. 2008;4(2):139–45. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2008.02.002
- Chiu H-W, Xia T, Lee Y-H, Chen C-W, Tsai J-C, Wang Y-J. Cationic Polystyrene Nanospheres Induce Autophagic Cell Death through the Induction of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Nanoscale. 2015;7(2):736–46. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR05509H
- Prata JC. Airborne MPs: Consequences to Human Health? Environ Pollut. 2018;234:115–26. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.043
- Farhat SCL, Silva CA, Orione MAM, Campos LMA, Sallum AME, Braga ALF. Air Pollution in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: a Review. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;11(1):14–21. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2011.06.008
- Fernandes EC, Silva CA, Braga ALF, Sallum AME, Campos LMA, Farhat SCL. Exposure to Air Pollutants and Disease Activity in Juvenile-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Arthritis Care Res. 2015;67(11):1609–14. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.22603
- Bernatsky S, Smargiassi A, Barnabe C, Svenson LW, Brand A, Martin RV, et al. Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease in Two Canadian Provinces. Environ Res. 2016;146:85–91. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.12.021
- Campanale C, Massarelli C, Savino I, Locaputo V, Uricchio VF. A Detailed Review Study on Potential Effects of Microplastics and Additives of Concern on Human Health. IJERPH. 2020;17(4):1212. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041212
- MohanKumar SM, Campbell A, Block M, Veronesi B. Particulate Matter, Oxidative Stress and Neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology. 2008;29(3):479–88. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2007.12.004
- Deng Y, Zhang Y, Lemos B, Ren H. Tissue Accumulation of Microplastics in Mice and Biomarker Responses Suggest Widespread Health Risks of Exposure. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):46687–710. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46687
- Chang C. The Immune Effects of Naturally Occurring and Synthetic Nanoparticles. J Autoimmun. 2010;34(3):J234–46. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2009.11.009
- Browne MA, Crump P, Niven SJ, Teuten E, Tonkin A, Galloway T, et al. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ Sci Technol. 2011;45(21):9175–9. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/es201811s
- Cole M, Lindeque P, Halsband C, Galloway TS. Microplastics as Contaminants in the marine Environment: A Review. Mar Pollut Bull. 2011;62(12):2588–97. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.09.025
- Barshtein G, Livshits L, Shvartsman LD, Shlomai NO, Yedgar S, Arbell D. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Activate Erythrocyte Aggregation and Adhesion to Endothelial Cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2016;74(1):19–27. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0705-6
- Wick P, Malek A, Manser P, Meili D, Maeder-Althaus X, Diener L, et al. Barrier Capacity of Human Placenta for Nanosized Materials. Environ Health Perspect. 2010;118(3):432–6. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901200
- Monti DM, Guarnieri D, Napolitano G, Piccoli R, Netti P, Fusco S, et al. Biocompatibility, Uptake and Endocytosis Pathways of Polystyrene Nanoparticles in Primary Human Renal Epithelial Cells. J Biotechnol. 2015;193:3–10. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.11.004
Figures:
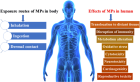
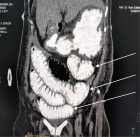
Figure 1
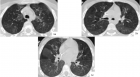
Figure 2
Figure 3
Similar Articles
-
Impact of Microplastics on Human Health through the Consumption of Seafood: A ReviewNeeraj Kumar*,Dev Brat Mishra. Impact of Microplastics on Human Health through the Consumption of Seafood: A Review. . 2025 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001036; 9: 015-019
Recently Viewed
-
Hypoglycemia by Ginseng in type 2 Diabetic Patient: Case ReportAngelo Michele Carella*,Teresa Marinelli,Armando Melfitano,Michele Di Pumpo,Matteo Conte,Angelo Benvenuto. Hypoglycemia by Ginseng in type 2 Diabetic Patient: Case Report . New Insights Obes Gene Beyond. 2017: doi: 10.29328/journal.hodms.1001001; 1: 001-006
-
Unveiling Disparities in WHO Grade II Glioma Care among Physicians in Middle East and North African (MENA) Countries: A Multidisciplinary SurveyFatimah M Kaabi,Layth Mula-Hussain*,Shakir Al-Shakir,Sultan Alsaiari,Leonidas Chelis,Renda AlHabib,Sara Owaidah,Renad Subaie,Marwah M Abdulkader,Ibrahim Alotain. Unveiling Disparities in WHO Grade II Glioma Care among Physicians in Middle East and North African (MENA) Countries: A Multidisciplinary Survey. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001048; 10: 001-005
-
Analysis and Control of a Glucose-insulin Dynamic ModelLakshmi N Sridhar*. Analysis and Control of a Glucose-insulin Dynamic Model. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001033; 10: 010-016
-
NAD⁺ Biology in Ageing and Chronic Disease: Mechanisms and Evidence across Skin, Fertility, Osteoarthritis, Hearing and Vision Loss, Gut Health, Cardiovascular–Hepatic Metabolism, Neurological Disorders, and MuscleRizwan Uppal,Umar Saeed*,Muhammad Rehan Uppal. NAD⁺ Biology in Ageing and Chronic Disease: Mechanisms and Evidence across Skin, Fertility, Osteoarthritis, Hearing and Vision Loss, Gut Health, Cardiovascular–Hepatic Metabolism, Neurological Disorders, and Muscle. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001032; 10: 001-009
-
Nasal cytology in patients with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection: occurrence of atypical lymphocytesArturo Armone Caruso*, Anna Miglietta, Giovanni De Rossi, Liliana Nappi, Veronica Viola, Stefano De Rossi, Salvatore Del Prete, Clara Imperatore, Sabato Leo, Daniele Naviglio, Monica Gallo, Daniela Marasco, Lucia Grumetto. Nasal cytology in patients with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection: occurrence of atypical lymphocytes. Adv Treat ENT Disord. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.ated.1001014; 7: 001-006
Most Viewed
-
Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trialSathit Niramitmahapanya*,Preeyapat Chattieng,Tiersidh Nasomphan,Korbtham Sathirakul. Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001026; 7: 00-007
-
Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and RehabilitationCristina Popescu, Mircea-Sebastian Șerbănescu, Gigi Calin*, Magdalena Rodica Trăistaru. Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and Rehabilitation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001030; 8: 004-012
-
Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging PresentationKarthik Baburaj*, Priya Thottiyil Nair, Abeed Hussain, Vimal MV. Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging Presentation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001029; 8: 001-003
-
Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-goDaniel Gandia,Cecilia Suárez*. Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-go. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001033; 7: 001-002
-
The benefits of biochemical bone markersSek Aksaranugraha*. The benefits of biochemical bone markers. Int J Bone Marrow Res. 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001013; 3: 027-031

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."